The COUNTA function is one of the counting functions in Excel that counts all non-empty cells in a range.
Whether you’re working with text, numbers, dates, or even error values, COUNTA will count them all as long as the cell isn’t completely empty.
When to Use Excel COUNTA Function
COUNTA function can be used when you want to count all the cells in a range that are not empty. This is particularly useful for:
- Counting survey responses – regardless of whether they contain text, numbers, or dates
- Data validation – ensuring all required fields have been filled
- Progress tracking – monitoring how many items in a list have been completed
- Attendance tracking – counting entries in attendance sheets
- Quality control – verifying data entry completion
What COUNTA Function Returns
It returns a number that represents the number of cells that are not empty in the specified range(s).
Syntax
=COUNTA(value1, [value2], [value3], …)
where:
- value1 – the first item, cell reference, or range within which you want to count the number of cells that are not empty.
- [value2], … – (optional) up to 255 additional items, cell references, or ranges within which you want to count the number of cells that are not empty.
Example 1: Count Non Blank Cells in a Range
Let’s start with a simple example.
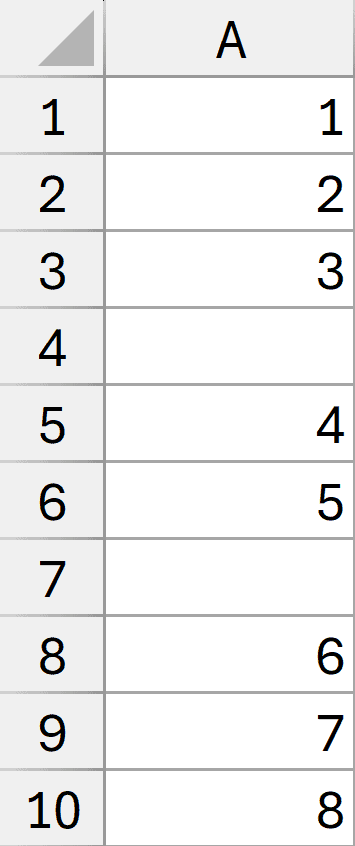
Below I have a dataset, and I want to count the total number of non-empty cells in the range A1:A10.
Here is the formula that will do this.
=COUNTA(A1:A10)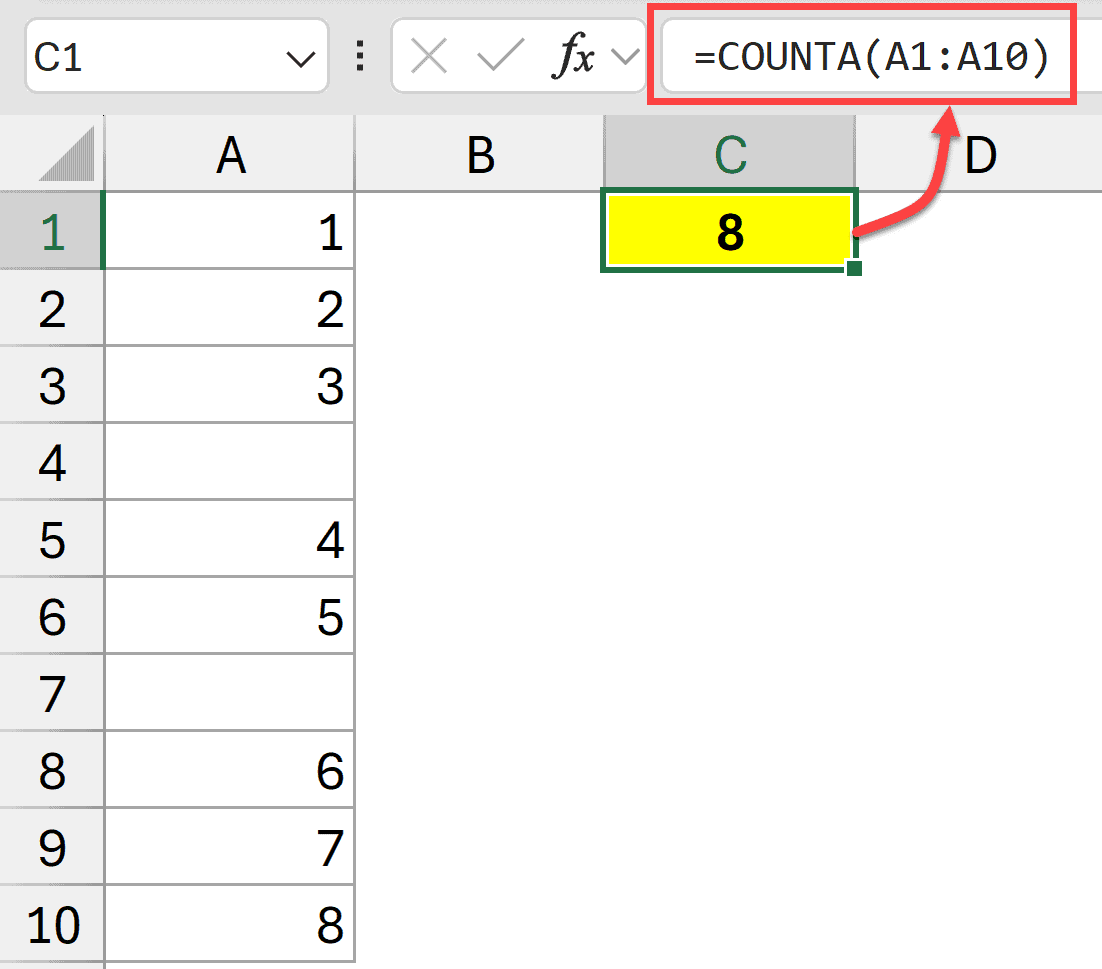
This counts all non-empty cells in the range A1:A10.
Pro Tip: If you want to count all the non-blank cells in the entire column, you can use =COUNTA(A.:.A)
Example 2: Count Non Blank Cells in Multiple Ranges
Below I have numbers in Column A and Column C, and I want to count all the non-blank cells in these two ranges.
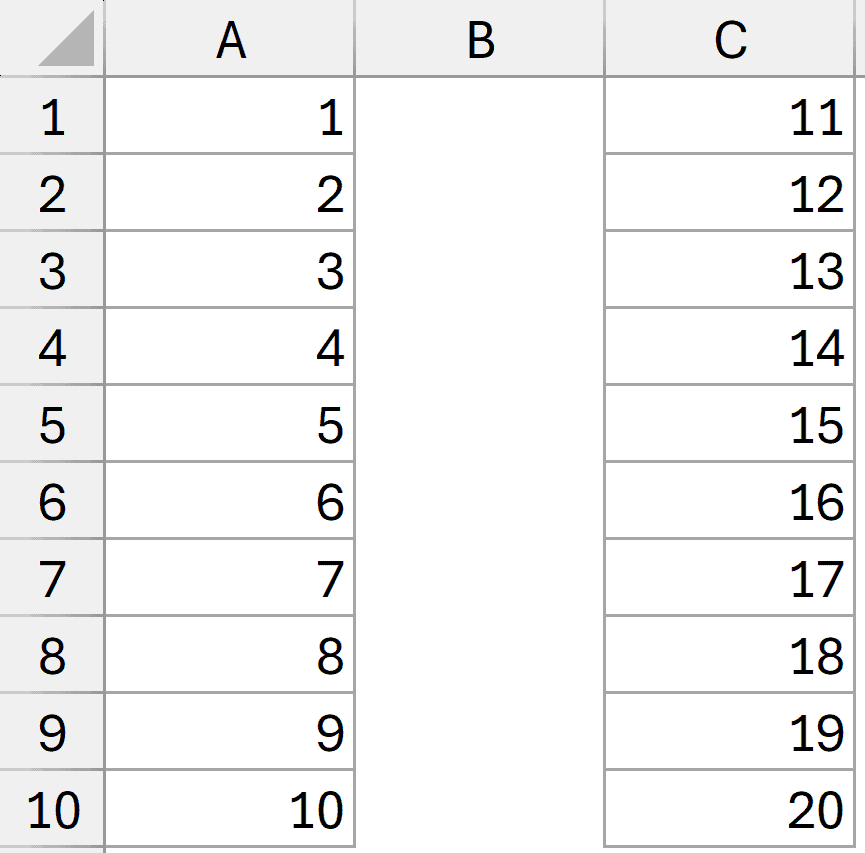
I can use multiple ranges within a single COUNTA function, as shown below.
=COUNTA(A1:A10, C1:C10)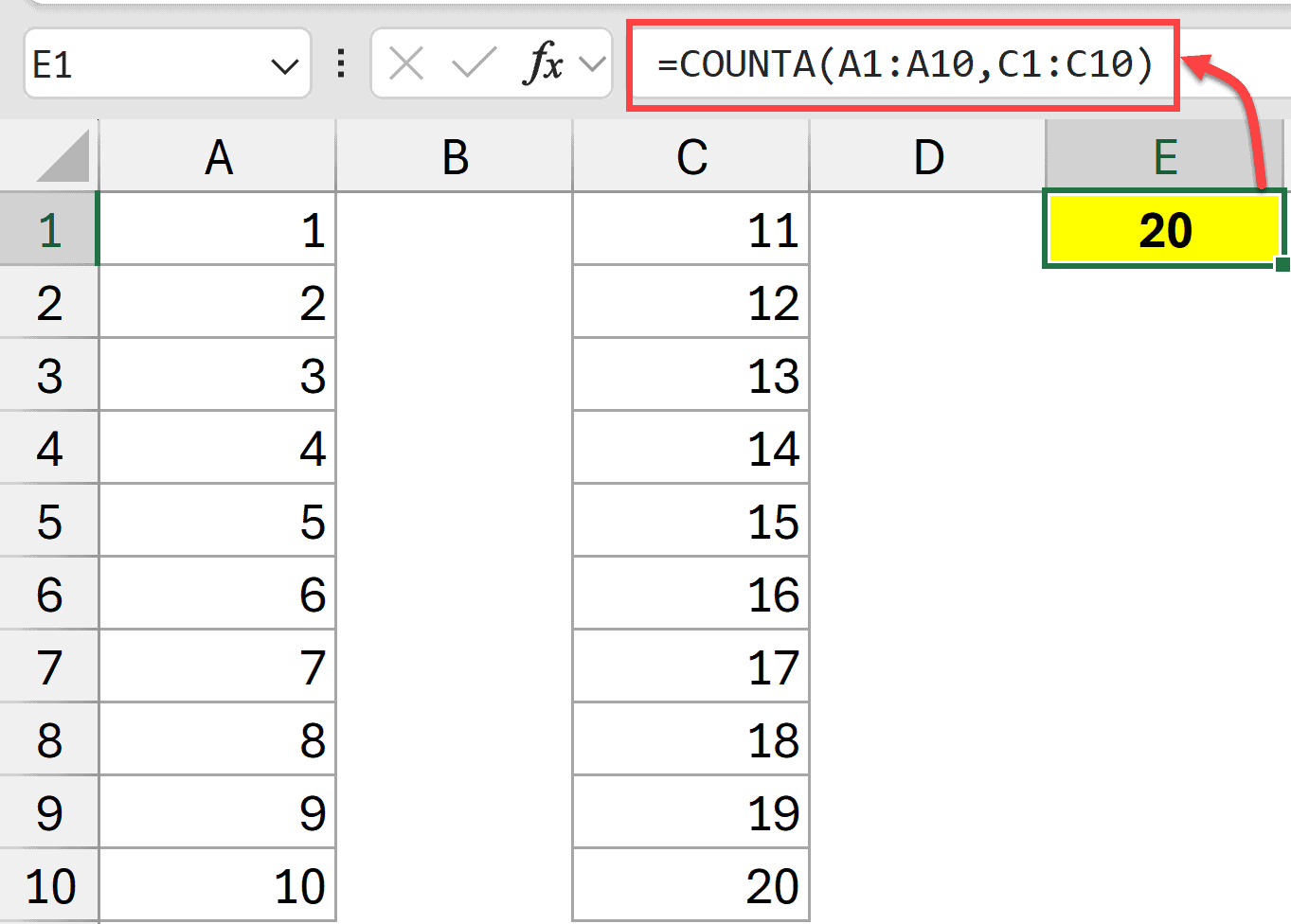
This will count all the non-empty cells across all the multiple separate ranges specified in the formula.
Example 3: Count Non Blank Cells with Mixed Data Types
Below I have a dataset where I have different types of data types in the cells, including text, error, number, date, and Boolean value.
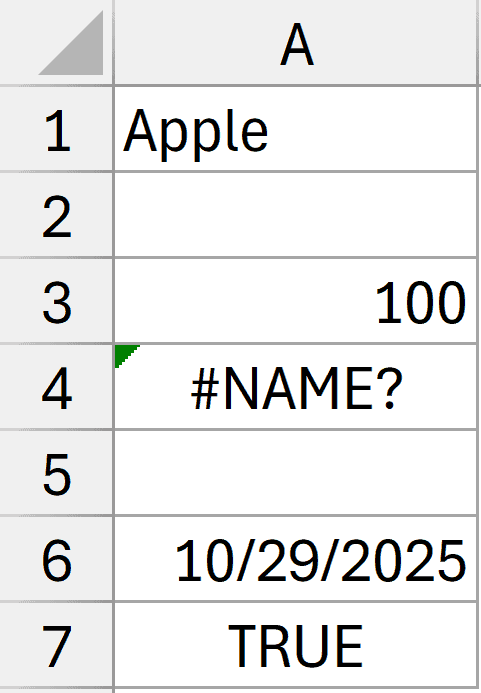
Here is the formula that will count all the non empty cells:
=COUNTA(A1:A7)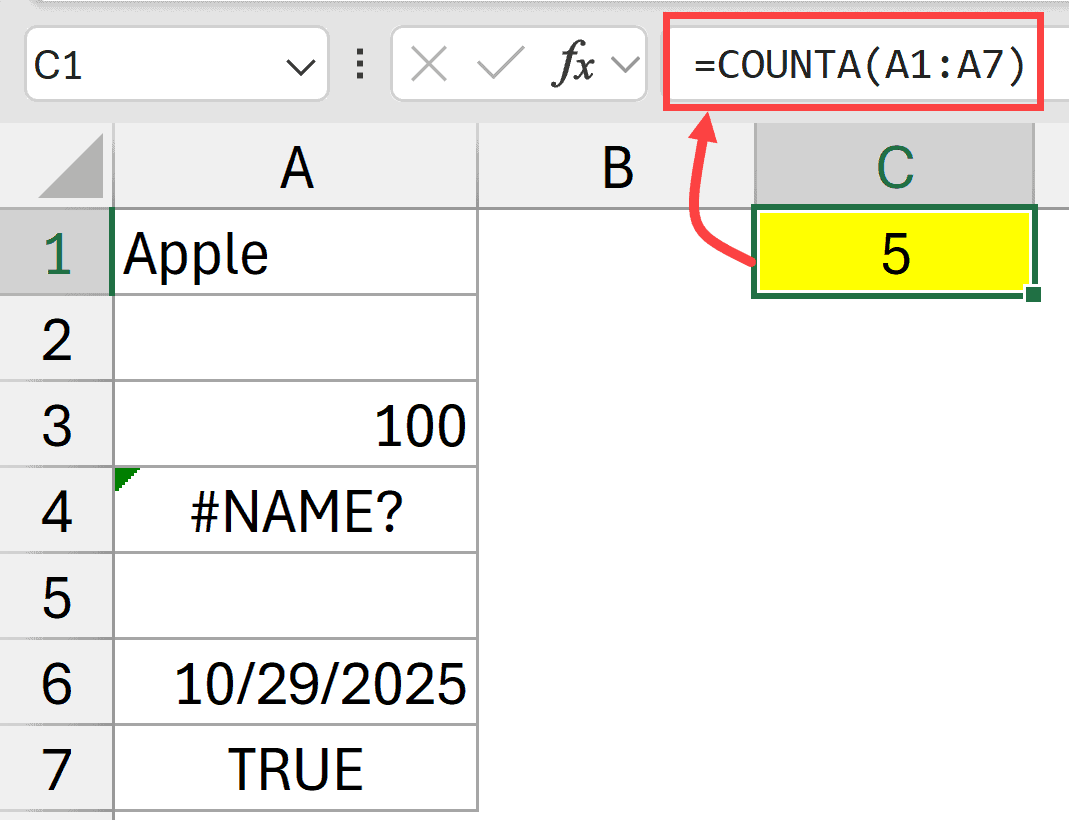
Example 4 – Number all the Filled Cells / Rows
Below I have a dataset where I have some data in column B, and I want to add a serial number in the cells in column A only if the cell in column B is filled. If the cell in column B is empty, I do not want to put any number on it.
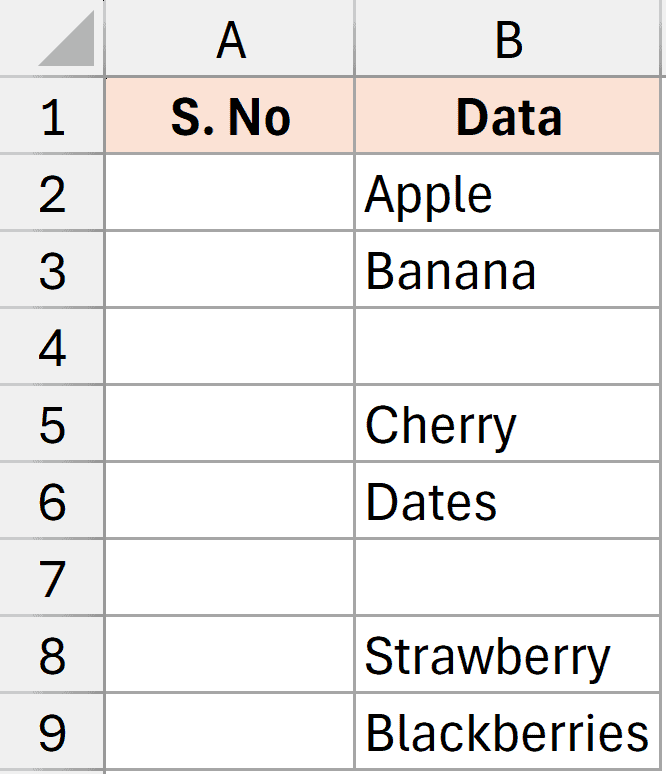
Here is the formula that will do this.
=IF(ISBLANK(B2), "",COUNTA($B$2:B2))
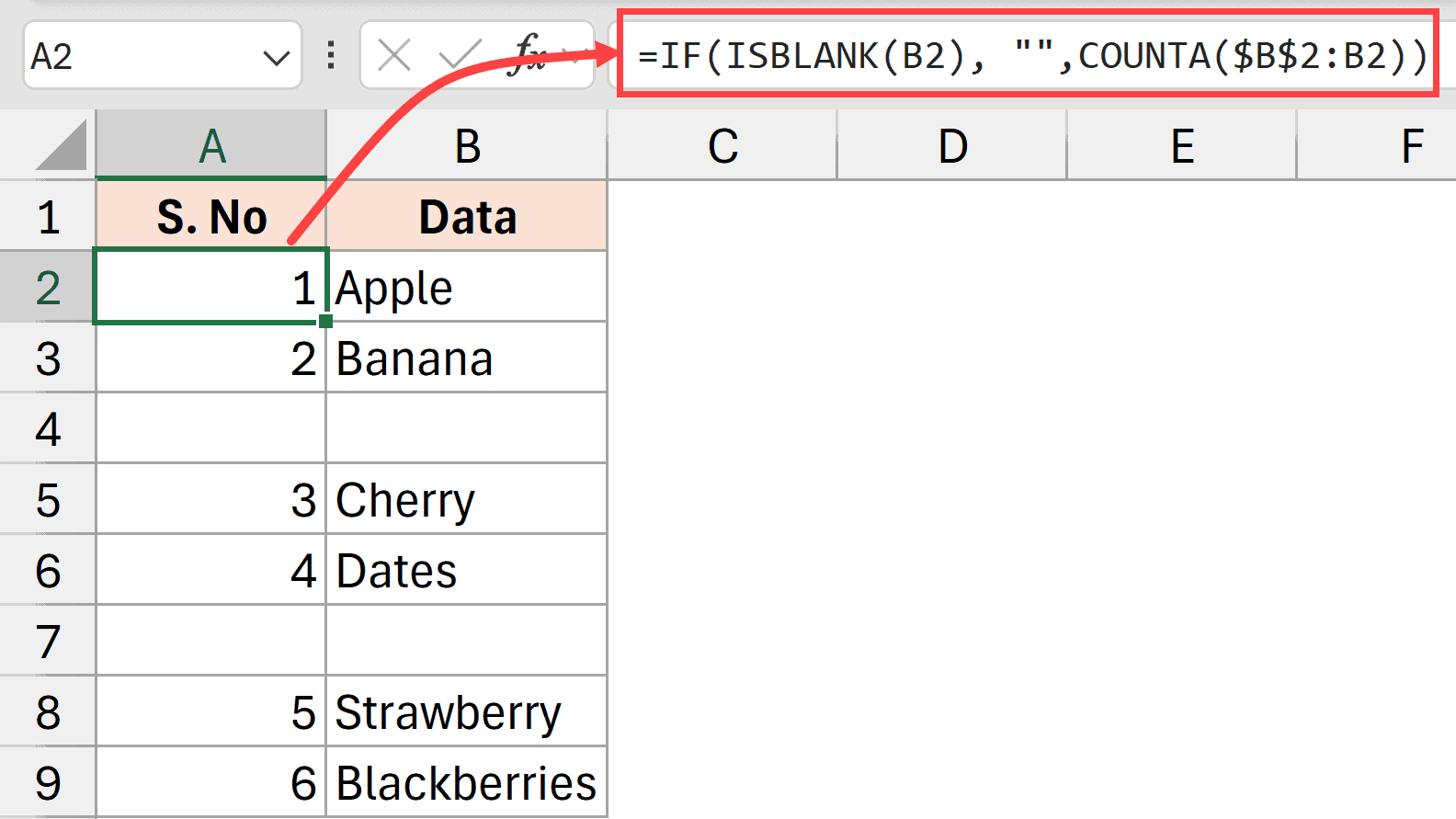
The above formula first checks whether cell B2 is empty or not using the ISBLANK function. If the cell is empty, it returns a null string. But if it is not empty, it uses the COUNTA function to count all the filled cells starting from cell B2.
This gives us a sequential serial number for all the filled cells while skipping the blank cells.
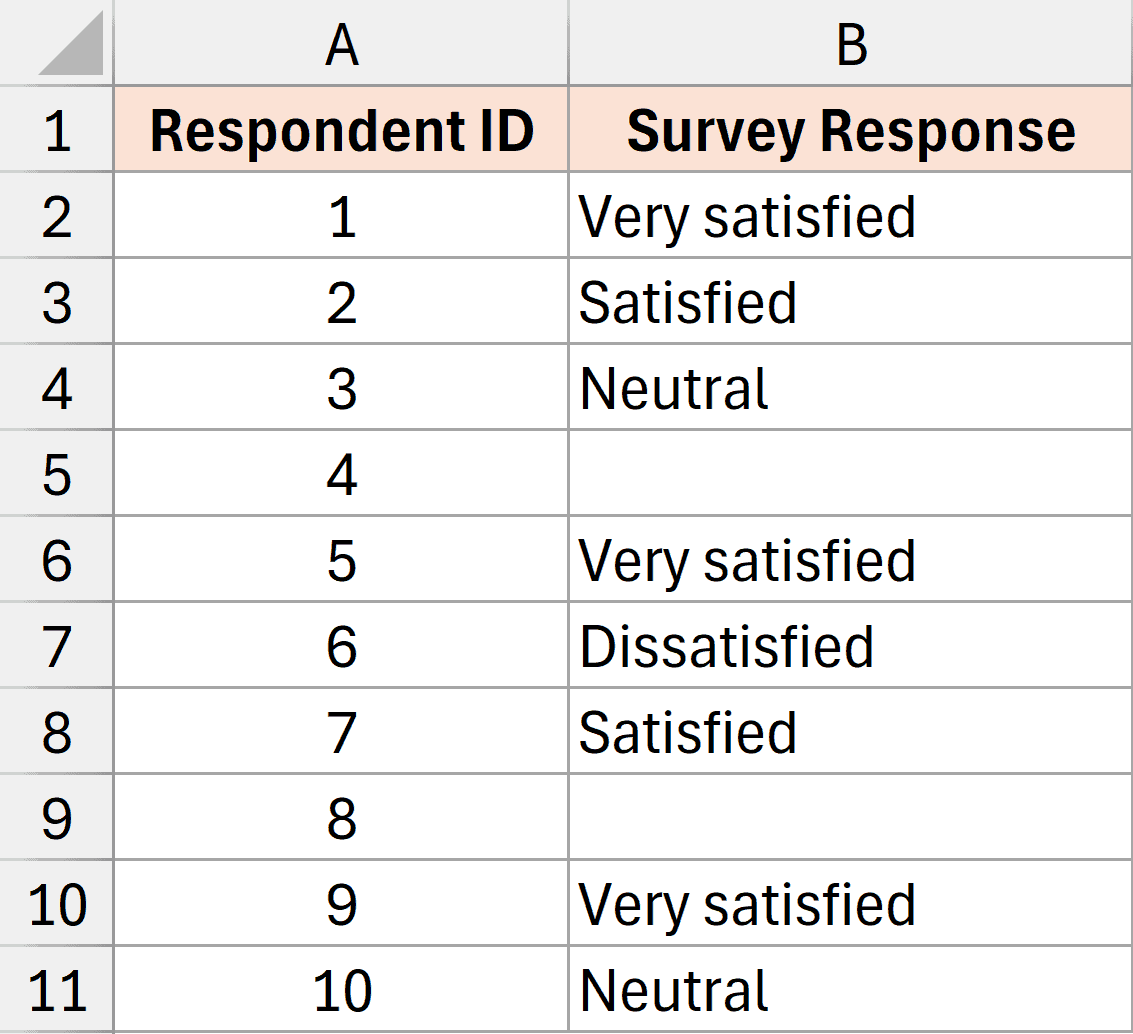
Example 5: Survey Response Tracking
You can also combine the result of the COUNTA function with a text string to get insights about your data.
For example, below I have a dataset where I have survey responses, and I want to know how many survey responses I have received.
Below is a formula that could give the result of the counter function and then append the string to give me insights about the data.
=COUNTA(B2:B50) & " responses received"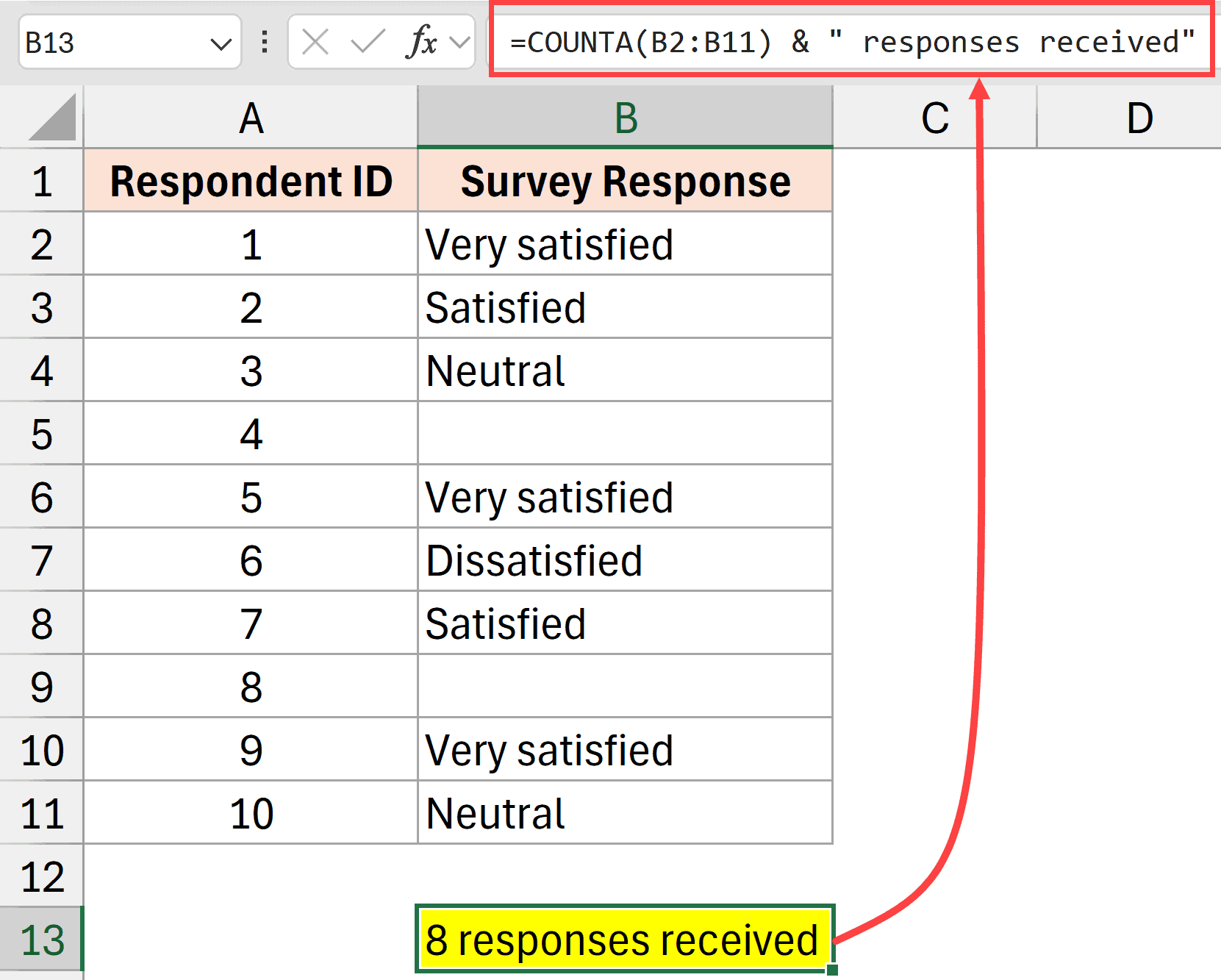
Additional Notes
- Counts all non-empty cells – If a cell contains any type of information including error values, it is counted by COUNTA
- Empty string handling – If a formula returns an empty string (“”), that cell is still counted by COUNTA
- Performance tip – For large datasets, specify exact ranges instead of entire columns (use A1:A1000 instead of A:A). Or use the TRIMREF function or the dot operator to ensure that blank cells around the ranges are ignored
- Hidden data – COUNTA counts cells that appear empty but contain spaces or non-visible characters
Related Excel Functions:
- Excel COUNT Function – Count numeric values only
- Excel COUNTBLANK Function – Count empty cells
- Excel COUNTIF Function – Count with criteria
- Excel COUNTIFS Function – Count with multiple criteria
Other Excel articles you may also like: