One of my friends works in a healthcare analytics company. He often connects with me on some of the real-life issues he faces while working with data in Excel.
A lot of times, I convert his queries into Excel tutorials on this site, as it could be helpful for my other readers as well.
This is also one such tutorial.
My friend called me last week with the following issue:
There is address data in a column in Excel, and I want to identify/filter cells the where the address has duplicate text strings (words) in it.
Here is the similar dataset in which he wanted to filter cells that have a duplicate text string in it (the ones with red arrows):
Now what makes this difficult is that there is no consistency in this data. Since this is a compilation of data sets that have been manually created by sales reps, there can be variations in the dataset.
Consider this:
- Any text string could repeat in this dataset. For example, it could be the name of the area or the name of the city or both.
- The words are separated by a space character, and there is no consistency in whether the city name would be there after six words or eight words.
- There are thousands of records like this, and the need is to filter those records where there are any duplicate text strings.
After considering many options (such as text to columns and formulas), I finally decided to use VBA to get this done.
So I created a custom VBA function (‘IdDuplicate’) to analyze these cells and give me TRUE if there is a duplicate word in the text string, and FALSE in case there are no repetitions (as shown below):
This custom function analyzes each word in the text string and checks how many times it occurs in the text. If the count is more than 1, it returns TRUE; else it returns FALSE.
Also, it has been created to only count words more than three characters.
Once I have the TRUE/FALSE data, I can easily filter all the records that are TRUE.
Now let me show you how to do this in Excel.
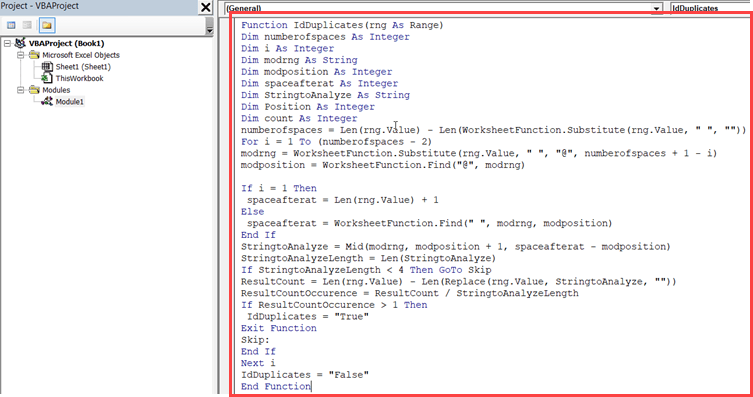
VBA Code for the Custom Function
This is done by creating a custom function in VBA. This function can then be used as any other worksheet function in Excel.
Here is the VBA code for it:
Function IdDuplicates(rng As Range) As String Dim StringtoAnalyze As Variant Dim i As Integer Dim j As Integer Const minWordLen As Integer = 4 StringtoAnalyze = Split(UCase(rng.Value), " ") For i = UBound(StringtoAnalyze) To 0 Step -1 If Len(StringtoAnalyze(i)) < minWordLen Then GoTo SkipA For j = 0 To i - 1 If StringtoAnalyze(j) = StringtoAnalyze(i) Then IdDuplicates = "TRUE" GoTo SkipB End If Next j SkipA: Next i IdDuplicates = "FALSE" SkipB: End Function
Thanks Walter for suggesting a better approach to this code!
How to Use this VBA Code
Now that you have the VBA code, you need to place it in the backend of Excel, so that it can work as a regular worksheet function.
Below are the steps to put the VBA code on the backend:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on Visual Basic (you can also use the keyboard shortcut ALT + F11)
- In the VB Editor back end that opens, right-click on any of the workbook objects.
- Go to ‘Insert’ and click on ‘Module’. This will insert the module object for the workbook.
- In the Module code window, copy and paste the VBA code mentioned above.
Once you have the VBA code in the back end, you can use the function – ‘IdDuplicates’ as any other regular worksheet function.
This function takes one single argument, which is the cell reference of the cell where you have the text.
The result of the function is TRUE (if there are duplicate words in it) or FALSE (if there are no duplicates). Once you have this list of TRUE/FALSE, you can filter the ones with TRUE to get all the cells that have duplicate text strings in it.
Note: I have created the code only to consider those words that are more than three characters long.
This ensures that if there are 1, 2, or 3 character-long words (such as 12 A, K G M, or L D A) in the text string, these are ignored while counting the duplicates. If you want, you can easily change this in the code.
This function will only be available in the workbook where you have copied the code in the module. In case you want this to be available in other workbooks as well, you need to copy and paste this code in those workbooks.
Alternatively, you can also create an add-in (enabling this function to be available in all the workbooks on your system).
Also, remember to save this workbook in .xlsm extension (since it has a macro code in it).
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Excel Advanced Filter – A Complete Guide with Examples.
- Dynamic Excel Filter Search Box – Extract Data as you Type
- Remove Duplicates Within a Cell in Excel
- Paste into Filtered Column (Skipping Hidden Cells) in Excel
- The Ultimate Guide to Find and Remove Duplicates in Excel.
- Separate First and Last Name in Excel (Split Names Using Formulas)
- Check IF Cell Contains Partial Text in Excel









18 thoughts on “How to Filter Cells that have Duplicate Text Strings (Words) in it”
Sir, I have column of integer values and they are up yo 4 decimal places. I have duplicate issue with values. how to remove duplicate in this case?
Hi I have used the above code, if second word has comma, it is not setting as True. could you please help me on this.
Example : test test, – False
You are wonderful! So useful!
Can I get VBA learning from the very basics?
Hey Aniruddha.. You can get some tutorials here. I am currently working on creating basic step-by-step tutorials on VBA. Will start posting in the next 2 weeks. You can subscribe to my email list to get notified.
Really useful. Thank you very much….!!!
really nice code and it does a great job. It would help us a lot if you would go a little more into detail of what the various parts of the code do – e.g. (modrng = WorksheetFunction.Substitute(rng.Value, ” “, “@”, numberofspaces + 1 – i) – so some value = some other value(some value, space, ?@?, #spaces+1-count) ???
Hey Rich,
I have updated the code and now it’s shorter and easier to read
Nice you all tutorial thanks of help .
Glad you’re finding the tutorials useful!
Yes, But can you share more tutorial about SQL and Pl/SQL topics.
Hey Mithilesh.. I only create tutorials on MS Excel.
This takes advantage of the Split function in vba. It could be streamlined more.
Function IdDuplicates2(rng As Range)
Dim StringtoAnalyze As Variant
Dim i As Integer
On Error Resume Next
IdDuplicates2 = “False”
StringtoAnalyze = Split(rng.Value, ” “)
i = LBound(StringtoAnalyze)
If UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – LBound(StringtoAnalyze) > 0 Then
Do While i <= UBound(StringtoAnalyze) And IdDuplicates2 = "False"
If StringtoAnalyze(i – 1) = StringtoAnalyze(i) Then IdDuplicates2 = "True"
i = i + 1
Loop
End If
End Function
Thanks for sharing Ben.. I agree, Split and Lbound/Ubound could be a cleaner approach. I tried your code but it didn’t work. returns TRUE in all cases. Also, the one I have considers that any words (at any position could repeat). So it the same word could be at 2nd and 5th position, and it will be highlighted.
The code of Ben needs a small change, the start value for i must be LBound(StringToAnalyze) + 1:
Function IdDuplicates2(rng As Range)
Dim StringtoAnalyze As Variant
Dim i As Integer
On Error Resume Next
IdDuplicates2 = “False”
StringtoAnalyze = Split(rng.Value, ” “)
i = LBound(StringtoAnalyze) + 1
If (UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – LBound(StringtoAnalyze)) > 0 Then
Do While i <= UBound(StringtoAnalyze) And IdDuplicates2 = "False"
If StringtoAnalyze(i – 1) = StringtoAnalyze(i) Then
IdDuplicates2 = "True"
Exit Do
End If
i = i + 1
Loop
End If
End Function
Hey Wouter.. Thanks for sharing. Your code works 🙂 But it still only identifies cells where the repetition in adjacent words. In case these words are not adjacent, it returns TRUE
I concur on that, but made an other function to look for repeated words in any place of the cell contents:
Function IdRepeated(rng As Range) As Boolean
Dim StringtoAnalyze As Variant
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Const minWordLen As Integer = 4
On Error Resume Next
IdRepeated = False
StringtoAnalyze = Split(rng.Value, ” “)
‘ remove short words from array
For i = (UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – 1) To LBound(StringtoAnalyze) Step -1
If Len(StringtoAnalyze(i)) < minWordLen Then
For j = i To UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – 1
StringtoAnalyze(j) = StringtoAnalyze(j + 1)
Next
ReDim Preserve StringtoAnalyze(UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – 1)
End If
Next
j = UBound(StringtoAnalyze)
If (Len(StringtoAnalyze(j)) < minWordLen) Then
ReDim Preserve StringtoAnalyze(j – 1)
End If
' Look for repeated words
For i = LBound(StringtoAnalyze) To UBound(StringtoAnalyze) – 1
For j = i + 1 To UBound(StringtoAnalyze)
If (StringtoAnalyze(i) = StringtoAnalyze(j)) Then
IdRepeated = True
Exit Function
End If
Next
Next
End Function
Thanks Wouter.. I used the SPLIT function to approach this. Here is the code that’s also working (and is shorter too)
Also made a change to identify words even if in different cases.
Function IdDuplicates(rng As Range) As String
Dim StringtoAnalyze As Variant
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Const minWordLen As Integer = 4
StringtoAnalyze = Split(UCase(rng.Value), ” “)
For i = UBound(StringtoAnalyze) To 0 Step -1
If Len(StringtoAnalyze(i)) < minWordLen Then GoTo SkipA For j = 0 To i - 1 If StringtoAnalyze(j) = StringtoAnalyze(i) Then IdDuplicates = "TRUE" GoTo SkipB End If Next j SkipA: Next i IdDuplicates = "FALSE" SkipB: End Function Will update on the site soon.